Decentralized Finance or DeFi is booming recently with the volume of DEX transactions growing by over 900% in 2021 compared to 2020. The interest in DeFi remains high in 2022 with DEX transaction volumes in USD this year remaining on par with 2021 volumes, despite the drop in crypto prices.
This hype seems to be attracting not only investors, but also hackers, looking for quick and supposedly “untraceable” gains. In Q2 2022 their focus shifted entirely to exploitation of DeFi services and protocols for profit, as was observed by the Research Team at BestBrokers.com, while looking into data from the most recent report by Chainalysis. We follow the path of DeFi’s share in stolen crypto from non-existent to 100% and explain the reasoning behind this fact below.
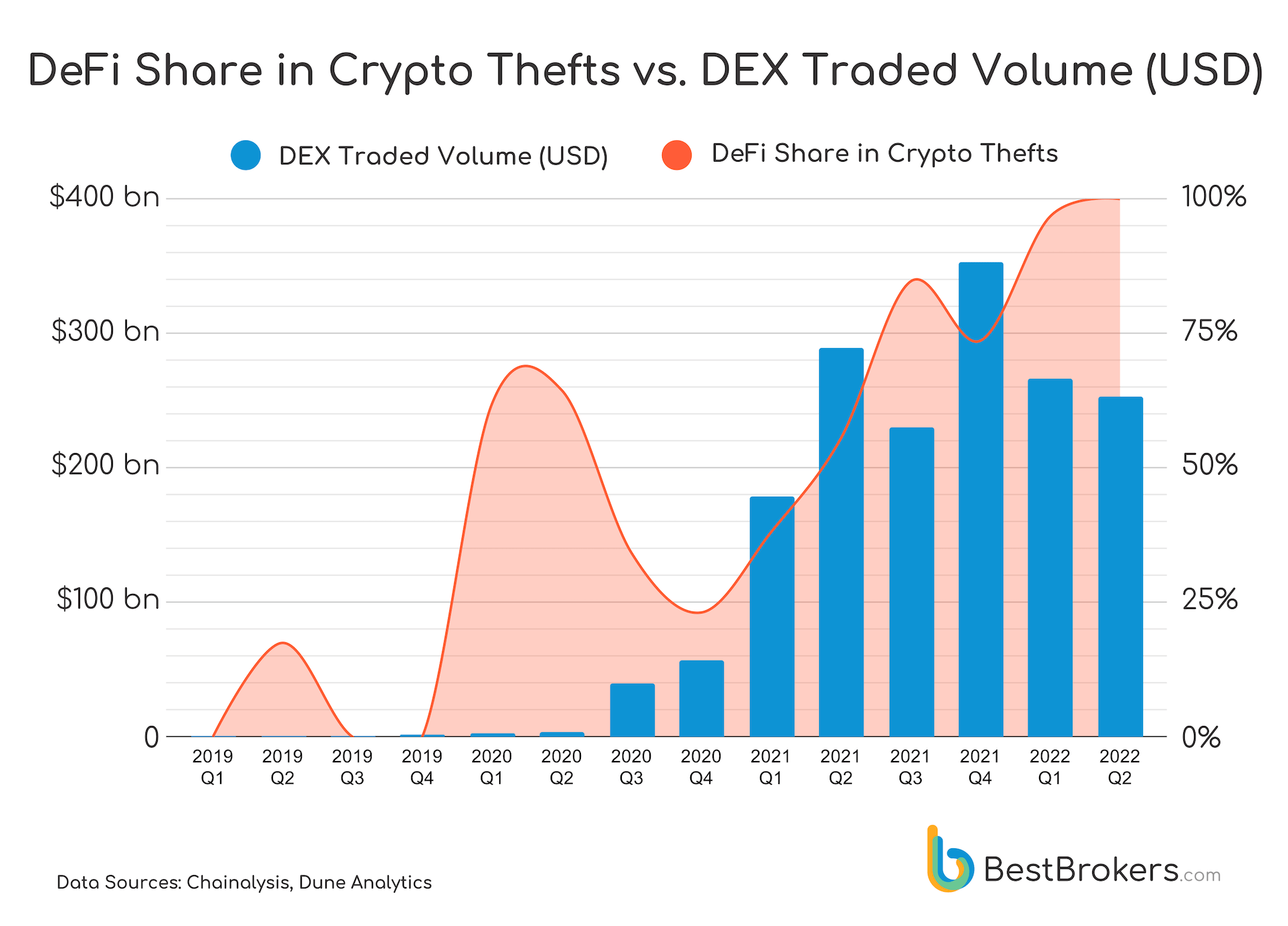
Why is DeFi favored by hackers?
Decentralized Finance apps aim to provide alternatives to traditional banking services at a fraction of the cost. They do that by utilizing Blockchains that support Smart Contracts – these are in essence programs residing in the Blockchain, that run when specific conditions are met. Typically they are used to execute agreements between different parties, usually involving transfer of cryptocurrencies. Thus the Smart Contract plays the role of the intermediary with the only expense being the gas fees involved in the contract’s on-chain operations plus possibly some minor service fee.
This sounds great in theory, however in practice DeFi has been haunted by security issues that may jeopardize its growth despite the very promising adoption rates and traded volumes. Here are the essential reasons why:
DeFi is still an emerging technology and not many people can program Smart Contracts well
DeFi was made possible in 2015 by the Ethereum blockchain, which first added support for Smart Contracts. This new concept required new and complex programming languages such as Solidity and Vyper, which started emerging only after the fall of 2014. These languages are still undergoing rapid changes and updates. Solidity, for example, has been getting new releases and updates monthly.
This makes the learning curve very shallow and it takes developers more time and effort to learn such a language.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) have an additional public weak spot, compared to centralized ones
As the DeFi services’ Smart Contracts reside at public addresses, their program logic may be subject to reverse-engineering even if their code is not made public. This means that anyone with enough skills may end up with the contract’s complete machine code and potentially find and exploit a security hole.
DeFi tokens may be subject to market manipulation
Often DeFi services utilize one or more of their own tokens, used in some way in the service’s ecosystem such as to incentivize staking by paying users a fixed interest rate or to algorithmically peg a token to the USD. As these tokens often have market value and are traded at exchanges and liquidity pools, they may be subject to price manipulation for gain by an illicit party and affect the entire DeFi project negatively.
Anyone may run a DeFi service and start collecting deposits in crypto
You only need a website, running a Web3 Decentralized App and a Smart Contract and with the right ad and marketing budgets you may start acquiring users right away. Someone with ill intentions from the beginning may pose as a legitimate project, collect investments and at one point disappear with all the crypto.